CSS Animation Performance — CheatSheet
Here’s a comprehensive table of CSS properties categorized by their impact on browser rendering performance, specifically focusing on Layout, Paint, and Composite:
- Layout: Calculate the size and position of elements on the page.
- Paint: Draw the page into graphical layers — essentially individual images that make up the page.
- Composite: Draw these layers to the viewport.
Properties
clip-path,opacity,transform,z-index,visibility,filter, are best for performing web animations
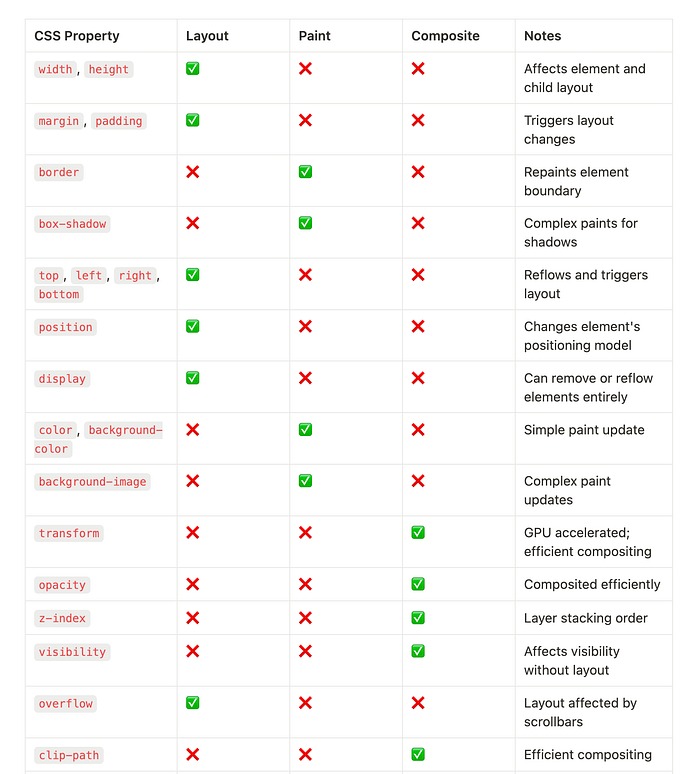
See the Full table at : CSS Properties Table
Legend:
- ✅: Triggers the specified phase
- ❌: Does not trigger the phase
Performance Tip:
- Prefer transform and opacity changes for animations instead of properties like
top,left, orwidthto avoid costly layout recalculations. - Reduce unnecessary paints and layout reflows by using GPU-accelerated properties (
transform,opacity). transformandopacityare cheapest to render in all browsers. Browsers are improving the rendering performance of other styles (and SVG) all the time, withfilter,background-colorandclip-pathon the horizon.
How to use Will-change ?
The will-change css property hints to browsers how an element is expected to change. Browsers may set up optimisations before an element is actually changed.
/* Keyword values */
will-change: auto;
will-change: scroll-position;
will-change: contents;
will-change: transform; /* Example of <custom-ident> */
will-change: opacity; /* Example of <custom-ident> */
will-change: left, top; /* Example of two <animatable-feature> *//* Global values */
will-change: inherit;
will-change: initial;
will-change: revert;
will-change: revert-layer;
will-change: unset;You can hint to the browser that they should create a new layer by setting the willChange style to "transform":
element.style.willChange = "transform"Instead of animating boxShadow, animate filter with the drop-shadow function:
// ❌
#box:hover { boxShadow: "10px 10px black" };
// ✅
#box:hover { filter: "drop-shadow(10px 10px black)" };Browser Rendering :
1. Layout (Reflow)
Definition:
The layout phase calculates the position and size of elements in the document based on the CSS and DOM structure.
When It’s Triggered:
- Adding, removing, or changing the size/position of elements (
width,height,margin,padding, etc.). - Resizing the window or changing the font size.
Performance Impact:
- Expensive, as it affects the entire document or subtree of elements.
- Causes reflow for child elements when dimensions change.
2. Paint (Repaint)
Definition:
The paint phase involves filling in pixels for visual elements, such as colors, borders, text, and shadows.
When It’s Triggered:
- Changes to visual properties that don’t affect the layout (
color,background-color,border,box-shadow).
Performance Impact:
- Moderate cost as it redraws only the visual parts of elements but doesn’t impact the layout.
3. Composite (Layer Composition)
Definition:
The composite phase involves assembling the different painted layers on the GPU to display the final image on the screen.
When It’s Triggered:
- GPU-accelerated properties such as
transform,opacity, andfilter.
Performance Impact:
- Least expensive as it avoids recalculating layout or repainting.
- Efficiently handled by the GPU for smoother animations.
